
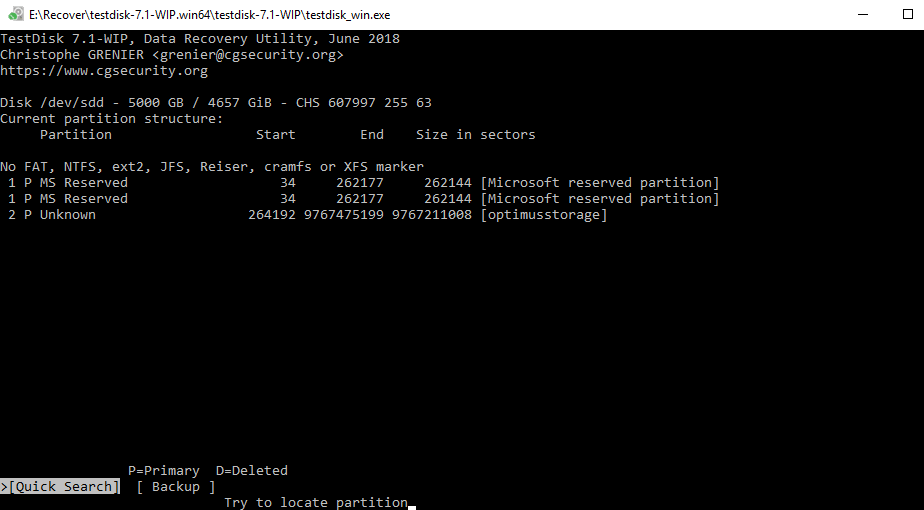
As ext2/ext3/reiserfs/jfs share the same filesystem type: 0x83, TestDisk has to check for each filesystem. Entry number 2 is reserved for the whole disk.įollowing the filesystem type, TestDisk runs some basic checks on the boot sector/superblock of each filesystem. Sun label can have up to 8 partition entries. TestDisk also checks that no partition data shows a partition as ending after the end of the disk, and that none of them are overlapping each other. The partition entries are read using the logical start and size in sectors, then TestDisk checks to see if the logical values match the CHS values. TestDisk checks that each value is in the authorized range: i.e., no sector value less than 1 nor higher than the number of sectors per head. Modern operating systems and BIOS chips use LBA mode to access the data, but FAT12/16/32 boot sectors still make reference to CHS geometry. Only one primary partition can have the boot flag set.ĬHS information storage is limited to a maximum of 1024 cylinders The MBR and each extended partition must end with the two bytes 0x55 and 0xAA, in that order which make up the hex word 0xAA55 (since x86 CPU systems are little-endian). Each logical partition is contained by an extended partition/container.

One of the entries can be an extended partition allowing several logical partitions. The Intel partition structure is composed of the MBR table and extended partitions. None (i.e.: small media without partition) TestDisk can handle several type of partitions: TestDisk's Analyse does a quick check of the partition structure. *=Primary bootable P=Primary L=Logical E=Extended D=DeletedĪnalyzes a drive's current partition structure and finds partitions, making it possible to recover lost partitions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
